| Quercus palustris | |
| Author | Muenchh. 1770 Hausvater 5: 253 |
| Synonyms | rubra var. palustris (Muenchh.)
Kuntze 1891 rubra var. dissecta Lam. 1785 |
| Local names | pin-oak
; |
| Range | NE
United States; 0-350 m; introduced in Europe in 1800; |
| Growth habit | 15-20
m tall (may reach 40 m); crown conical, with lower branches drooping,
upper branches ascending; |
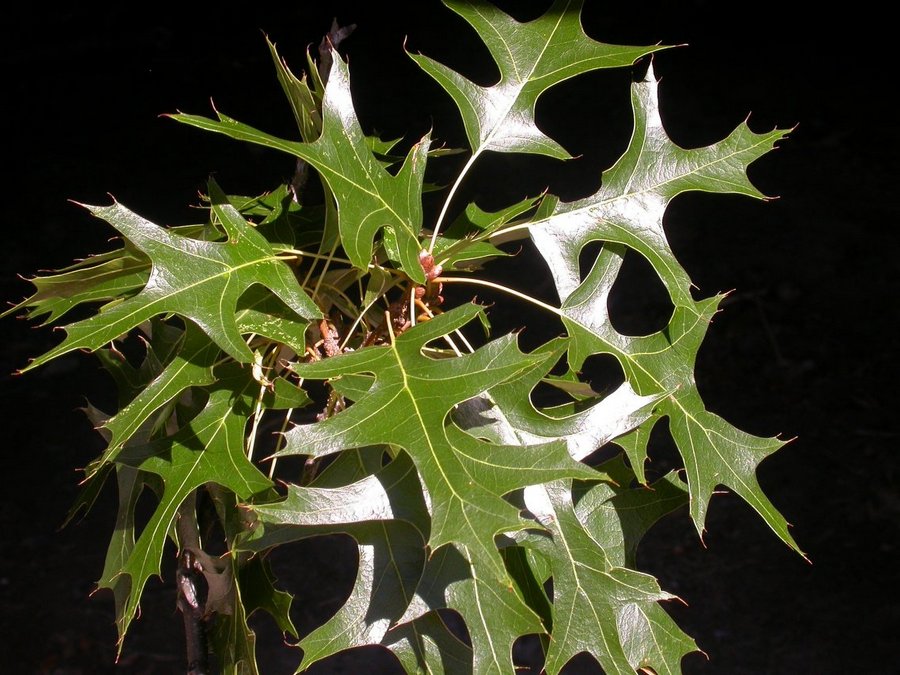
| Leaves | 7.5-13
x 5-10 cm; apex obtuse or acuminate; base cuneate;2-3 pairs of pointed
lobes and deep U-shaped sinuses reaching three-quarters the distance to
the midvein; lobes at middle leaf are wider, at right angle with the midrib;
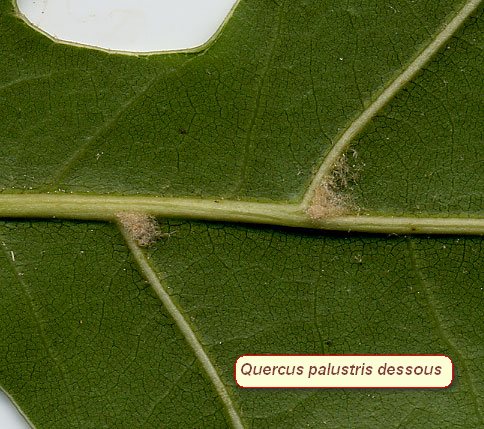
shiny green above, paler beneath with light brown tufts of hairs at axils
of veins; petiole slender, glabrous, 3-5 cm long; |
| Flowers | spring;
|
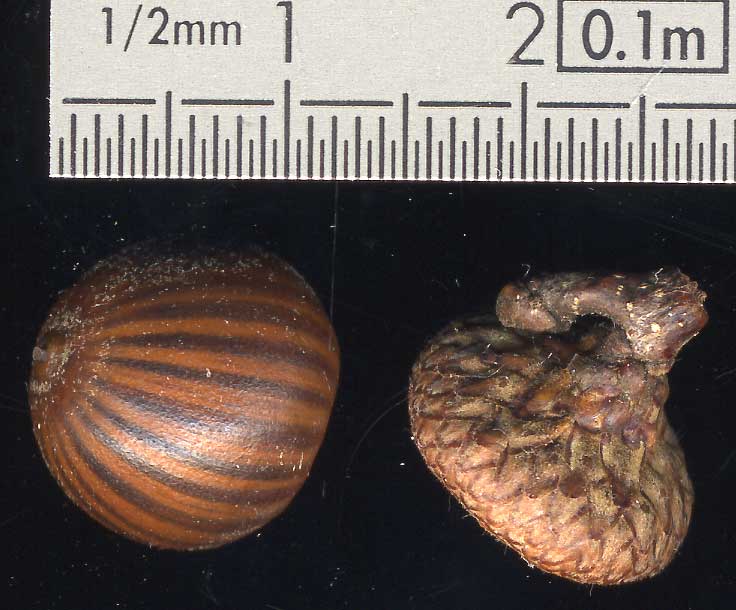
| Fruits | acorn
1.2 cm long, 1.5 cm wide, rounded, often striate; one or several together,
on short peduncle; cup shallow with appressed scales, covering the base
of the small nut; |
|
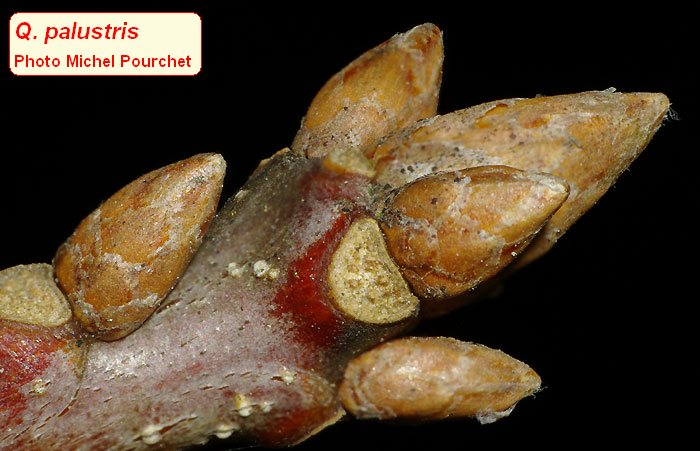
Bark, twigs and |
bark smooth, finely fissured, grey brown silvery; dead twigs remain on the tree ("pins"); twig slender, red brown becoming grey, glabrescent; termina bud brown, conical, pointed, hairless (Q. coccinea has hairy buds), 3-5 mm long; |
| Hardiness zone, habitat | hardy;
prefers moist soils; rather fast growing; |
| Miscellaneous | --A.Camus
: 421 -- Sub-genus Quercus, section Lobatae ; -- Resembles Q.coccinea, but it is easy to distinguish it from other red oaks = in the middle of the tree, the branches are at a right angle with the trunk, while the branches of the upper part of the tree are directed upwards, and the branches of the lower part are inclined towards the ground; -- Several hybrids, among them x exacta with Q.imbricaria, and x schochiana with Q.phellos ; |
| Subspecies and varieties |
_var. umbraculifera
Chancerel _var. compacta |
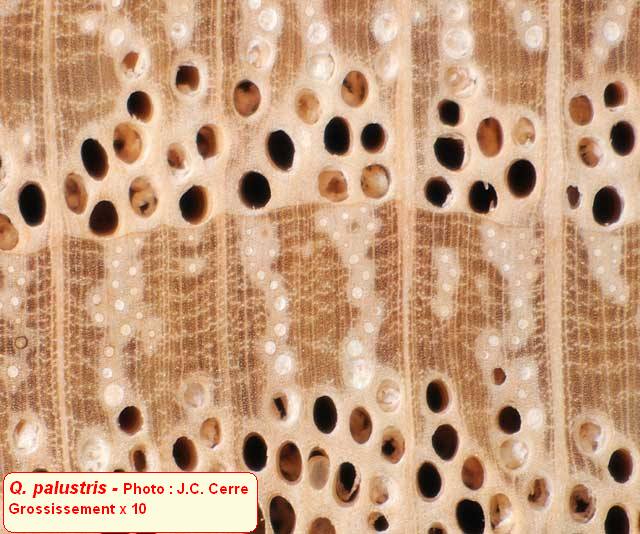
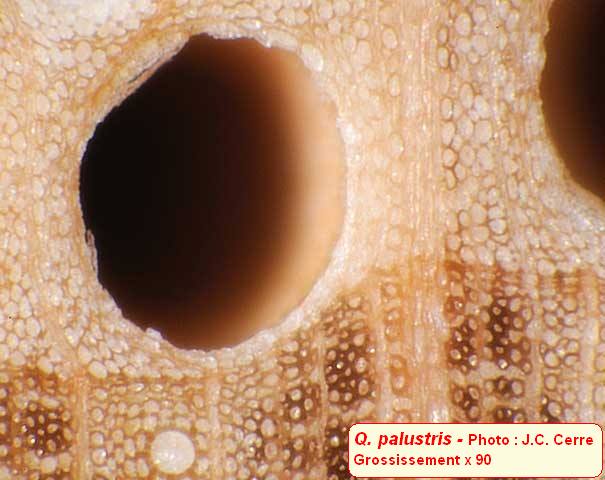
| Pictures |
|